Skeleton system
The skeleton of human being os composed about 206 bones.
Types of tissue that form the skeleton of human being: connective tissue proper, cartilage
Function of the skeleton: - to support (to protect rib cage and heart, lungs
- framework
- attachment per muscles, to keep a shape
- passive body movement
- blood formation - haemopoiesis
- mineral storage (Ca, P)
Structure of a bone
Composition of a bone: - a solid network of organic materials (25% - 30% of whole bone) - flexibility:
a) osteocytes
b) living tissue (spongy bone and compact bone)
c) collagenous fibres
- a matrix (innorganic content, about 50%-55% of whole body) - strength + hardness:
a) minerals - Ca, P
b) H2O - about 20 % of whole structure of bone
- with the growing age the amount of inorganic substances is decreasing - bones are more breakable
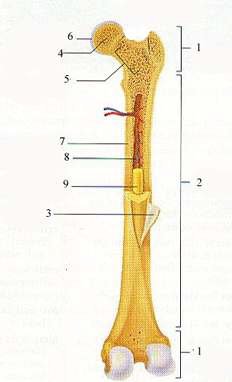 Structure of a bone:
Structure of a bone:
1. epiphysis
2. body (diaphysis)
3. periosteum - connective tissue, covers bone, contain many blood vessles, responsible for nourishment, nerve endings - sensitivity, responsible for external bone grow
4. spongy bone - quite porouse, cavities are filled by bone marrow, placed in epiphases of long bones and in short bones
5. red bone marrow - haemopoiesis, found in each bone of newborn but in adult it´s replaced by yellow bone marrow (is found in sternum, vertebra, pelvis, ribs and at the end of long bones)
6. cartilage - covers epiphases of bones, prevent friction
7. compact bone - very hard and dense
8. medullary cavity
9. yellow bone marrow - it contains fat
Internal bone growth
A bone is forming durong the process of ossification by the activity of osteoblasts that change cartilage to bone, ossification starts in the special platces = ossification centres.
The growth occurs in the epiphyseal disc = Growth plates (found in ossification centres) - it is under the control of growth hormone. It starts from the outside part and also inside part of the bone.
Classification of bones
according to the shape: a) short bones
b) long bones
c) flat bones
d) irregular bones
Types of Joints
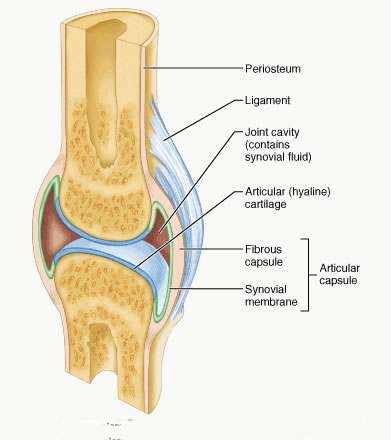 - place where 2 bones come together
- place where 2 bones come together
Classification is based on the amount of movement possible:
1. Fixed joint = synarthrosis
- immovable joint
- allows no movement between bones
- is held together by vonnective tissue
a) Connective tissue proper e.g. bones of skull
b) Cartilage e.g. ribs and sternum
c) Bone tissue e.g. pelvis, sacral bone
2. Semimovable joints = amphiarthrosis
- slightly movable joint
e.g. tibia + fibula
3. Freely movable joints = enables movement